SAML
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is an open standard for exchanging authentication and authorisation data.
The SAML release of SuperSTAR provides support for authenticating users via a third-party SAML identity provider.
Limitations in this Release
There are some limitations in this release:
-
SAML authentication is currently supported for SuperWEB2 only; it is not supported for the SuperADMIN Console or for SuperCROSS. This may be addressed in a future release, subject to customer requirements.
-
Open Data API access is not currently supported for SAML-authenticated users. Non SAML authenticated users can use the API.
-
Customers may encounter issues if they have local user accounts defined in SuperADMIN with IDs that clash with those of user accounts authenticated via SAML. This is an existing known issue with SuperSTAR’s authentication module functionality (for example it is also an issue when configuring authentication via Active Directory or LDAP). WingArc does not currently plan to address this issue: the recommended workaround is to ensure that the user IDs of SAML-authenticating users are different to those of any local user accounts.
-
For SAML authentication to work properly with SuperWEB2 account based features, the Identity Provider must be configured to use a persistent name ID. If the Identity Provider only supports transient name IDs then authentication will work, but users will not be able to retrieve their private saved tables on future logins (as they will log back in with a different ID).
Depending on customer requirements, this may be addressed in a future release (which would then treat users with transient IDs as guest users, with the account-based features disabled, rather than allowing them to save tables and custom data but not reload them).
You can use thenameIdFormatsetting in your authentication module to specify which attribute from the identity provider to use to uniquely identify users.
Configure SAML
Follow the steps below to set up SAML authentication:
Step 1 - Create SuperADMIN Authentication Service
The first step is to create an authentication service in the SuperADMIN console using the auth command. If you are working with multiple SAML identity providers (for example you have different providers for internal and external users, or different groups of external users connecting via different providers) then you will need to create a separate authentication service for each one.
Type the following command to create a new SAML authentication service:
auth add SAML <service_name>Replace <service_name> with a unique ID of your choice for this service. For example:
auth add SAML saml_keycloakStep 2 - Configure the Service
Use the following commands to configure the service parameters.
-
Each command starts with
auth <service_name>, where<service_name>is the name you selected in step 1 when you created the service. -
You can type
auth servicesorauth <service_name>at any time to review the settings you have already configured.
|
|
|
Replace For example:
|
|
|
|
A unique identifier for this entity to be configured on the SAML identity provider, enclosed in double quotes. In most cases you should follow these general best practice guidelines for creating an entity ID. If the SAML identity provider is only used internally then you may have your own entity ID format, in which case you should use that instead (if the identity provider is only used for this service, then the entity ID can use any format you wish). |
|
|
|
The URL that the user will be redirected to after successful login via the SAML identity provider. Set this to the full URL of your SuperWEB2 instance, followed by For example, if your SuperWEB2 server is available at https://myserver.com/webapi/ then the callback URL would be configured as follows:
|
|
|
|
The type of attribute used on the SAML identity provider for managing collections of permissions, enclosed in double quotes. This will typically be either
In the next section, you will use the |
|
|
|
(Optional). A delimiter used to split the If you choose to specify a delimiter, then the string in the SAML ticket will be split into individual groups using the delimiter character. For example, if the SAML ticket contains the following value:
Then you can split this into the individual groups
|
|
|
|---|
|
(Optional). Use a specific binding type ( If not specified, defaults to Supported values:
|
|
|
|---|
|
(Optional). The attribute to use as the name ID (unique ID for the user). You will need to ensure you have configured the identity provider accordingly for whatever value you set in SuperADMIN. If not specified, defaults to For example:
|
|
|
|
A mapping between the roles or groups on the identity provider and the corresponding local groups defined in SuperADMIN. These mappings can be based on information provided by the identity provider, but you should take care about how explicitly you configure the mappings, depending on how much you trust or control the identity provider. If you have not already done so, you will need to use the SuperADMIN console to create local groups as appropriate and define permissions for those groups. Configure the mappings in the form:
You can use the wildcard Following are some examples in order of safety: Map All Users to a Specific SuperADMIN Group For example: This will map all users who are authenticated through this identity provider (including users who are not part of any group) to a SuperADMIN group named This is the safest mapping as the identity provider has no control over the groups that users are assigned to. Map Specific Groups/Roles to Specific SuperADMIN Groups For example: This will map:
This type of mapping is reasonably safe even if you do not fully trust or control the identity provider as it only applies to specific groups that you explicitly define. You should be careful about mapping any groups to SuperADMIN’s Pass Through all Groups/Roles Unchanged
This will map all groups or roles on the identity provider to the corresponding SuperADMIN groups of the same name. This should only ever be used if you fully trust or control the identity provider. |
|
|
|---|
|
(Optional). A group of users from the identity provider who should have administrator-level permissions in SuperWEB2. If you choose to specify this setting, you must also ensure that the group is passed through to SuperADMIN using the If you do not set a value for Note that as SAML authentication is currently supported only for SuperWEB2 connections, the effect of designating users as administrators is currently limited to those users having access to all datasets in SuperWEB2. They will not be able to log in to the SuperADMIN console via the SAML-authenticated users. |
|
|
|---|
|
(Optional). The attribute from the identity provider to use as the display name for the user. For example:
CODE
The display name appears in the logout option on the menu in the top-right of SuperWEB2. By default, SuperWEB2 will attempt to use the display name attribute sent by the identity provider. In most cases this will work automatically and you will not need to set a value for You do not need to set the You should avoid changing the display name settings after going into production with SAML authentication as future changes to this setting will affect the ability of users to access their previously saved tables. |
Example Configuration
Following are some examples of complete configuration.
Map all users to one fixed SuperADMIN group:
auth saml_keycloak identityProviderMetadataPath "https://example.com/realms/master/protocol/saml/descriptor"
auth saml_keycloak entityId "https://example.com/idp"
auth saml_keycloak callbackUrl "https://myserver.com/webapi/rest/saml/login"
auth saml_keycloak groupMapping "*=keycloak_users"Map all users to one fixed SuperADMIN group, with an additional explicit mapping:
auth saml_keycloak identityProviderMetadataPath "https://example.com/realms/master/protocol/saml/descriptor"
auth saml_keycloak entityId "https://example.com/idp"
auth saml_keycloak callbackUrl "https://myserver.com/webapi/rest/saml/login"
auth saml_keycloak groupAttribute "Role"
auth saml_keycloak groupMapping "*=keycloak_users;subscribers=keycloak_subscribers"Step 3 - Export Metadata
Once you have completed the service configuration, you need to export the metadata for this service from the SuperADMIN configuration and upload this to the SAML identity provider.
-
Run the following command:
CODEauth <service_name> exportMetadata <filename>Replace
<service_name>with the name you selected in Step 1 when you created the service.You can use
<filename>to specify where to write the export, which can be any of the following:-
A filename of your choice (this will be written to the console working directory; if you installed to the default location on Windows, this will be C:\ProgramData\STR\SuperADMIN\console);
-
A relative path within the console working directory, followed by your chosen filename; or
-
Omit the filename, in which case the file will be written to
output/sp-metadata_<service_if>.xml
For example:
CODEauth saml_keycloak exportMetadata samlmetadata.xmlOnly locations within the console working directory are supported for the export. You can not use a file path to save the file to an arbitrary location on disk.
-
-
Locate the exported metadata file and upload it to the SAML identity provider you are using.
Step 4 - Configure SuperWEB2 Login
The next step is to configure how SuperWEB2 will present the different options on the login page. For example, you may want to:
-
Configure multiple different SAML services for different user groups.
-
Combine both standard logins (with a username and password), alongside SAML-based authentication.
-
Hide the SAML login options completely for general users, so only users with a special URL can login via SAML.
The structure of the login page is configured through login group configuration, which you define in SuperADMIN.
Default Login Page
By default, if you do not configure any login groups, SuperWEB2 simply displays an additional login button for each active SAML service with default button text that reads Log in with <service_name> (where <service_name> is the name you set in SuperADMIN).
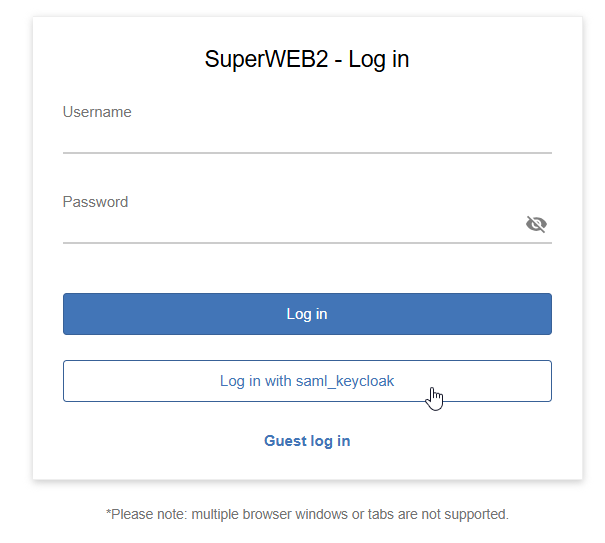
You can configure the text on this button by editing the settings in the messages.properties configuration file (located in <tomcat_home>\webapps\webapi\WEB-INF\classes\). You may need to edit multiple versions of this file for all the UI languages you support:
-
To change the Log in with text, edit the value of
page.login.loginWith.button.label(making sure to keep the{0}in the value, as this will be replaced with the corresponding service name:CODEpage.login.loginWith.button.label=Log in with {0} -
To set the display name for each configured service, add a new property in the format
loginService.<service_name>.displayName(where<service_name>matches the name you set in SuperADMIN). For example:CODEloginService.saml_keycloak.displayName=SAML
Defining Login Groups (Optional)
If you are happy with the default login page described above, where all SAML login options are displayed on a single page, alongside the regular logins, then you do not need to do any additional login configuration.
However, for more advanced settings, such as if you want to have multiple different login pages for different user groups, you will need to define your login structure in SuperADMIN. By default, when you set up multiple login pages, users will be able to access a drop-down list to select the appropriate group for them, but you can also choose to hide the link to this selector, in which case users will be able to access the appropriate group via a special URL.
Refer to the loginConfig command for more details on the options available and how to configure them. Some example configurations are shown below.
You can define the labels for any groups you create by adding a new property in the format loginGroup.<group_name>.displayName to messages.properties (and the corresponding localised versions of that file for other UI languages that you support). For example:
loginGroup.saml_logins.displayName=SAML LoginsExample loginGroups Configuration
Following are some example group configurations for various scenarios. Each example assumes you are starting from an empty configuration with no existing groups defined.
Step 5 - Activate the SAML Service in SuperADMIN
Once you have completed the configuration, the final step is to activate the SAML service in SuperADMIN, by setting the active parameter on the service to true:
auth <service_name> active true Replace <service_name> with the name you selected in Step 1 when you created the service. For example:
auth saml_keycloak active trueOnce you have activated the service, open the SuperWEB2 login page and verify that you can login using the SAML identity provider.
If you make changes to the configuration of your SAML auth service after you activate it, you will need to reload the configuration using the following command:
auth <service_name> reload
For example:
auth saml_keycloak reload
